Imagine a world where your daily commute is not only eco-friendly but also cost-effective and thrilling. Electric cars are revolutionizing the way you think about transportation.
Have you ever wondered how these silent, efficient vehicles work? You might be curious to know what’s happening under the hood when you press the accelerator and glide silently down the road. Understanding the mechanics behind electric cars can empower you with knowledge, making you a more informed consumer.
Dive into the fascinating world of electric vehicles and discover the surprising technology that powers your drive. You won’t want to miss the insights that could change the way you think about your next car.
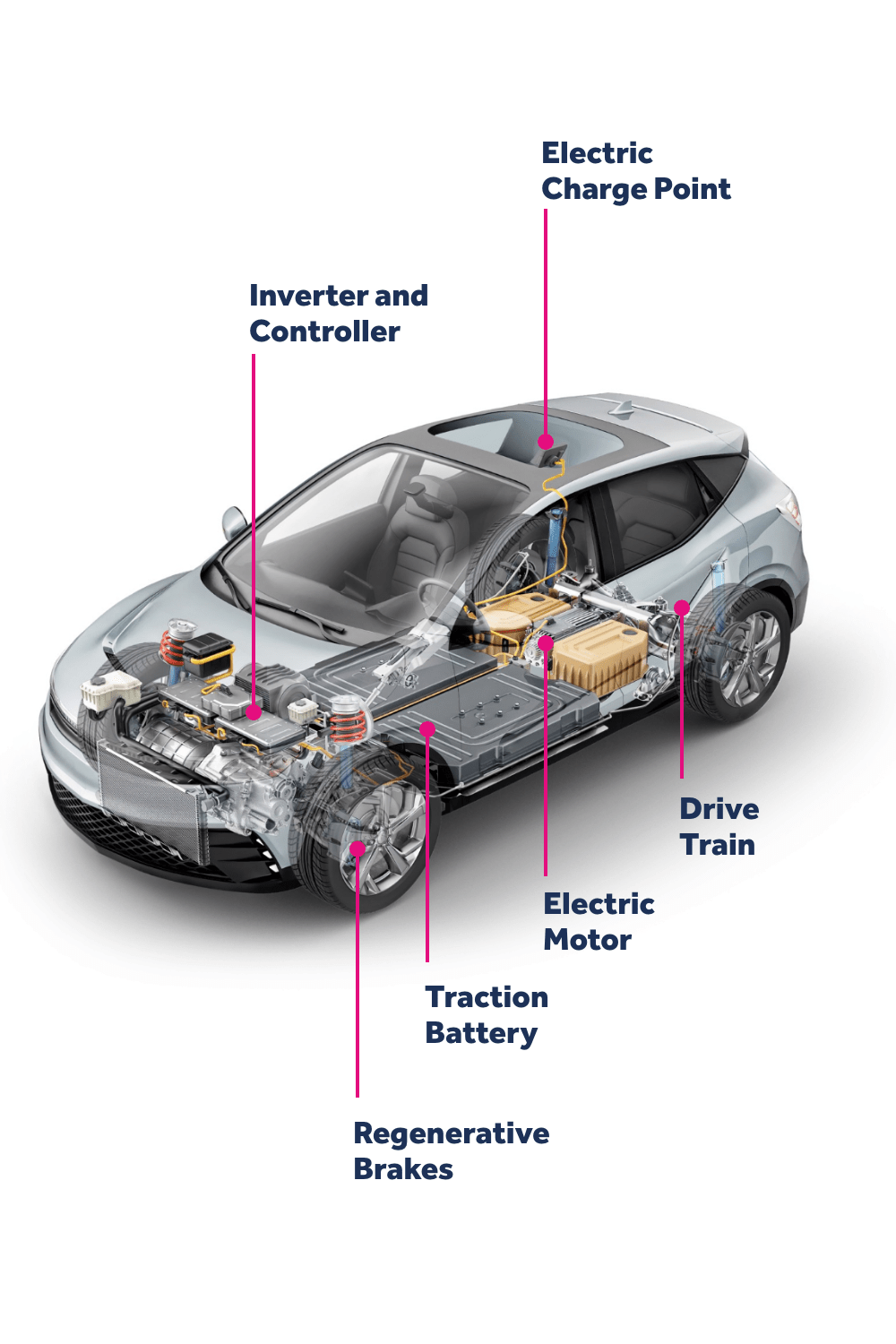
Electric Car Basics
Electric cars use electricity stored in batteries to power an electric motor. Unlike traditional engines, they produce no exhaust. Charging stations refill the battery, making them eco-friendly.
Electric Car Basics Electric cars are no longer just futuristic concepts; they’re becoming a part of our everyday reality. These vehicles are powered by electricity instead of traditional gasoline, which means they produce zero emissions while driving. But how exactly do they work? Understanding the basics can make you appreciate these technological marvels even more. Picture a world where you never have to stop at a gas station again. Intriguing, right?Components Of Electric Cars
Electric cars might seem complex, but they have fewer parts than traditional vehicles. The key components include: – Battery Pack: This is the heart of an electric car. It stores electricity to power the vehicle. Many cars use lithium-ion batteries, similar to those in your smartphone but much larger. – Electric Motor: This component converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy, which drives the wheels. Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors are quiet and efficient. – Charging Port: This is where you plug in the car to recharge the battery. Charging can be done at home or at public charging stations, making it as convenient as charging your phone overnight. – Controller: It acts as the brain, managing how much electricity flows to the motor. This ensures smooth acceleration and efficient power use.Types Of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) come in several types, each with unique features: 1. Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): These are fully electric with no gasoline engine. They rely solely on battery power. Examples include the Tesla Model 3 and Nissan Leaf. 2. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): These cars have both an electric motor and a gasoline engine. They can run on electric power for short distances, then switch to gasoline for longer trips. Think of the Chevrolet Volt. 3. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): Unlike PHEVs, these hybrids cannot be plugged in. They use regenerative braking to charge the battery. The Toyota Prius is a well-known example. Each type offers different advantages. Which type aligns with your lifestyle? Electric cars are reshaping our relationship with transportation. They offer a glimpse into a cleaner, more sustainable future. As you consider your next vehicle, it’s worth thinking about how these components and types fit into your life.Battery Technology
Electric cars are not just about sleek designs and zero emissions; at their heart lies cutting-edge battery technology. It’s this technology that powers your electric vehicle, allowing you to drive miles without a drop of gasoline. Understanding how these batteries work can deepen your appreciation for the innovation behind electric cars and help you make informed choices if you’re considering one.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the powerhouse of most electric cars today. They are renowned for their efficiency and ability to store large amounts of energy in a compact space. Have you ever wondered why your smartphone lasts all day? That’s lithium-ion technology at work. In electric cars, these batteries are scaled up to provide hundreds of miles of driving range. They recharge quickly and have a long lifespan, making them ideal for daily commutes or long road trips.
Manufacturers continually enhance these batteries to increase energy density and reduce weight. This means better performance and longer ranges for you. With advancements, some electric cars can now travel over 300 miles on a single charge. It’s like having the freedom to roam without worrying about running out of juice.
Battery Management Systems
Battery management systems (BMS) are the unsung heroes behind the efficiency of electric car batteries. They ensure that your battery performs optimally, keeping it safe and prolonging its life. Imagine having a personal assistant who keeps track of your calendar and reminds you of important tasks. A BMS does that for your car’s battery, monitoring its temperature, voltage, and charge cycles.
These systems prevent overcharging and overheating, which could otherwise damage the battery. They also balance the charge among all cells, ensuring uniform performance. Next time you drive your electric car, consider the role of BMS in providing a smooth and reliable experience.
Charging Infrastructure
Charging infrastructure is the backbone that supports electric cars, enabling you to keep moving. It’s not just about having a charger at home; it involves a network of stations across cities and highways. You might have noticed charging stations popping up in parking lots and malls. These facilities are crucial for long journeys, ensuring you can recharge anytime, anywhere.
Fast charging stations can replenish your car’s battery in under an hour, making them perfect for a quick pit stop during a road trip. Consider how this infrastructure impacts your lifestyle. With more stations, you can plan vacations without worrying about charging. The growing network is a testament to the increasing commitment to sustainable transport.
Battery technology in electric cars is more than just a technical marvel; it’s a gateway to a cleaner, more efficient future. As you explore electric vehicles, think about how this technology can transform your driving experience and contribute to a greener planet.
Electric Motors
Electric motors are the heart of electric cars, transforming electrical energy into mechanical energy. They provide the force that moves the car, offering smooth and quiet operation. Unlike traditional engines, electric motors are compact and efficient. Understanding how they work is crucial for grasping the basics of electric vehicles.
Types Of Motors Used
Electric cars typically use two types of motors: AC and DC motors. AC motors are common in modern electric cars. They are efficient and offer better speed control. DC motors are simpler, often found in older models. Both types convert electrical energy into motion, but AC motors are more advanced.
Motor Efficiency
Efficiency is a key advantage of electric motors. They convert a high percentage of electrical energy into motion. This means less energy waste compared to combustion engines. Efficient motors lead to longer battery life and better performance. Manufacturers aim for high efficiency to improve range and reduce charging needs.
Regenerative Braking
Regenerative braking is a smart feature in electric cars. It captures energy when slowing down or stopping. This energy goes back to the battery, extending driving range. It reduces wear on traditional brakes and improves efficiency. Drivers enjoy smoother braking and enhanced energy recovery.
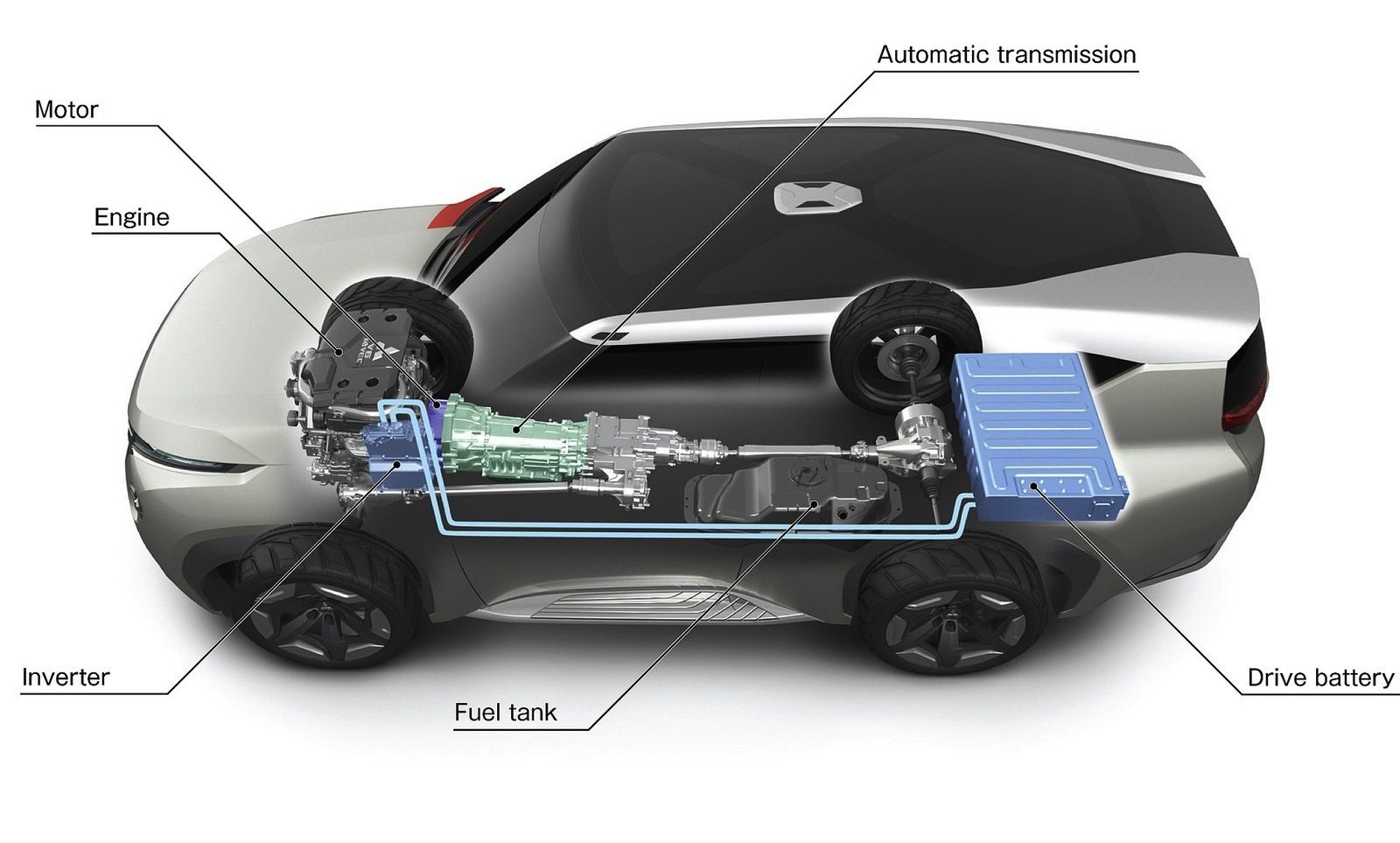
Power Electronics
Electric cars rely on power electronics to manage energy flow. Batteries store electricity, powering the motor for smooth driving. Efficient conversion of electrical energy into motion is essential, ensuring optimal performance and range.
Imagine gliding down the road in an electric car, the hum of the motor barely audible, powered by a complex system of electronics beneath the hood. Power electronics are the unsung heroes in electric vehicles, orchestrating the seamless conversion and management of electrical energy. They are the bridge between the battery and the electric motor, ensuring that your car runs efficiently and smoothly.Inverters And Converters
Inverters and converters are the backbone of your electric car’s power electronics. An inverter converts the direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) used by the electric motor. Think of it as the translator that enables your car to speak the language of speed and power. Converters, on the other hand, adjust the voltage levels of the DC power, ensuring that all components receive the correct voltage. Picture them as the diligent managers distributing the exact energy needed for each task.Role In Energy Management
Power electronics play a crucial role in managing your car’s energy consumption. They ensure that energy flows efficiently from the battery to the motor, optimizing performance and extending range. Have you ever wondered how your electric car brakes can recharge the battery? That’s the power electronics at work, capturing and redirecting energy back into the system. Efficient energy management means not just driving longer but also saving on energy costs. With power electronics, you’re not just driving a car; you’re part of a smarter, more sustainable future. Next time you hit the road in an electric car, consider the silent yet powerful role of power electronics. How do they impact the way you drive and the energy you consume?Drive Systems
Electric cars run using electric drive systems, converting battery power into motion. The electric motor propels the car, providing a smooth and quiet drive. Charging the battery is key to maintaining their energy-efficient performance.
Driving an electric car is a unique experience, and the magic lies in its drive system. At the heart of every electric vehicle (EV) is the motor, which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Understanding the different types of drive systems can help you appreciate the engineering marvel that powers your ride.Single Motor Systems
Single motor systems are the simplest form of electric drive systems. They use one electric motor to power either the front or rear wheels. This setup is similar to traditional internal combustion vehicles with front-wheel or rear-wheel drive. If you’re familiar with driving a car, you know the thrill of pressing the accelerator and feeling the vehicle respond. In a single motor system, that response is immediate and smooth. There’s no need for gear changes, offering a seamless driving experience. This system is often more efficient for everyday commuting. It provides enough power for most urban and suburban environments. Think about your daily drive—how often do you really need more than one motor?Dual Motor Systems
Dual motor systems elevate the driving experience by adding a second motor. Typically, one motor powers the front wheels, while the other powers the rear. This creates an all-wheel-drive system, offering enhanced traction and stability. Imagine driving on a rainy day. With a dual motor system, the vehicle automatically adjusts power between the two motors. This ensures optimal grip, giving you confidence in challenging conditions. Many performance-oriented electric cars feature dual motor systems for a reason. They deliver faster acceleration and better handling. If you crave speed and agility, this might be the system for you. Consider what matters most in your driving experience. Is it efficiency, or is it performance? Understanding these systems can guide your decision and enhance your journey. Are you ready to explore the potential of electric drive systems?Thermal Management
Electric cars use thermal management to keep their batteries at the right temperature. This system ensures efficient performance. By controlling heat, it helps extend battery life and improves the car’s overall efficiency.
Thermal management is crucial for the optimal functioning of electric cars. Imagine driving your electric vehicle on a hot summer day, and suddenly the performance drops or the battery overheats. Proper thermal management ensures that doesn’t happen. It helps maintain the right temperature for batteries and other components, ensuring smooth and efficient performance.Cooling Systems
Electric cars use sophisticated cooling systems to manage heat. These systems can include liquid cooling, air cooling, or a combination of both. Liquid cooling is often used because it efficiently transfers heat away from sensitive components like the battery. Have you ever touched a laptop that’s been running for a while and felt how hot it gets? Electric car batteries can get even hotter. Cooling systems prevent this by circulating coolant through a network of tubes around the battery. Another method is air cooling, which uses fans to blow air over the battery. Although simpler, it might not be as effective as liquid cooling in extreme temperatures. Both methods aim to keep the temperature stable, preventing overheating and preserving battery life.Impact On Performance
Thermal management directly affects your car’s performance. When an electric car’s battery overheats, it can lead to reduced efficiency and even damage. Efficient cooling systems help maintain performance by keeping the battery at an optimal temperature. Have you noticed how your phone’s battery drains faster when it heats up? Electric cars face similar challenges. Overheating can limit the power output, reducing acceleration and overall performance. Consider this: a well-managed thermal system can extend the lifespan of your car’s battery, saving you money in the long run. It’s not just about maintaining performance; it’s about ensuring your investment lasts longer. Wouldn’t you want your electric car to run efficiently for years to come? Incorporating effective thermal management in electric cars is like giving them a shield against temperature-related issues. It ensures that your vehicle performs at its best, regardless of the weather conditions. How do you think your daily drive would improve with a car that never overheats?Software And Controls
Electric cars operate using electric motors powered by batteries. Software and controls manage energy flow and optimize performance. Advanced systems ensure efficient power usage and enhance driving experience.
Electric cars are not just about batteries and motors; they’re a symphony of software and controls orchestrating every move. Imagine driving a car where your speed, safety, and comfort are all optimized by intelligent systems. Software in electric vehicles acts like the brain, processing data to enhance your driving experience. But how do these systems really work? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of vehicle control systems and smart features that make electric cars a marvel of modern engineering.Vehicle Control Systems
Vehicle control systems are the backbone of an electric car’s operations. They manage everything from acceleration to braking, ensuring smooth and efficient performance. These systems use sensors to gather data from various parts of the car. Think of them as the nerves sending signals to the brain. With this data, control systems make real-time adjustments. If you’ve ever felt a car seamlessly transition speeds or brake gently at the right moment, that’s the magic of these systems. They can optimize energy use, so you get the most miles out of every charge. How much control do you actually have over these systems, and does it enhance your driving experience?Smart Features
Electric cars are packed with smart features that not only make driving easier but also safer. Imagine a car that anticipates your needs before you even realize them. These features can include adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, and automatic emergency braking. Many electric cars can connect to your smartphone, allowing you to control aspects of the car remotely. Whether it’s pre-conditioning the cabin temperature or checking battery status, these features add convenience to your daily routine. Consider a scenario where you’ve left your car in a crowded parking lot. With smart parking assist, the car can maneuver into a tight spot with precision. Are these smart features something you’d find useful, or do they feel like an unnecessary luxury? The integration of software and controls in electric cars goes beyond simple automation. It’s about creating a seamless, intuitive driving experience that responds to you. As you get behind the wheel, these intelligent systems quietly work to ensure your journey is as enjoyable and efficient as possible.Environmental Impact
Electric cars are changing the way we view transportation. Their impact on the environment is a topic of much discussion. People are curious about how these vehicles affect our planet.
Electric cars do not produce tailpipe emissions. This is a major advantage over conventional cars. Yet, their complete environmental impact is more complex.
Carbon Footprint
Electric cars have a smaller carbon footprint. This is true during their lifetime compared to gasoline vehicles. They help reduce air pollution in cities. Their production process, though, can generate emissions.
Manufacturing electric cars often involves high energy consumption. This includes the extraction of raw materials. But, they offset these emissions over time. This happens through cleaner driving.
Battery Disposal
Batteries power electric cars and present disposal challenges. These batteries contain materials that need careful handling. Improper disposal can harm the environment.
Recycling programs are growing to address battery disposal. They aim to recover valuable materials. This reduces waste and conserves resources. Ensuring proper disposal is crucial for minimizing impact.
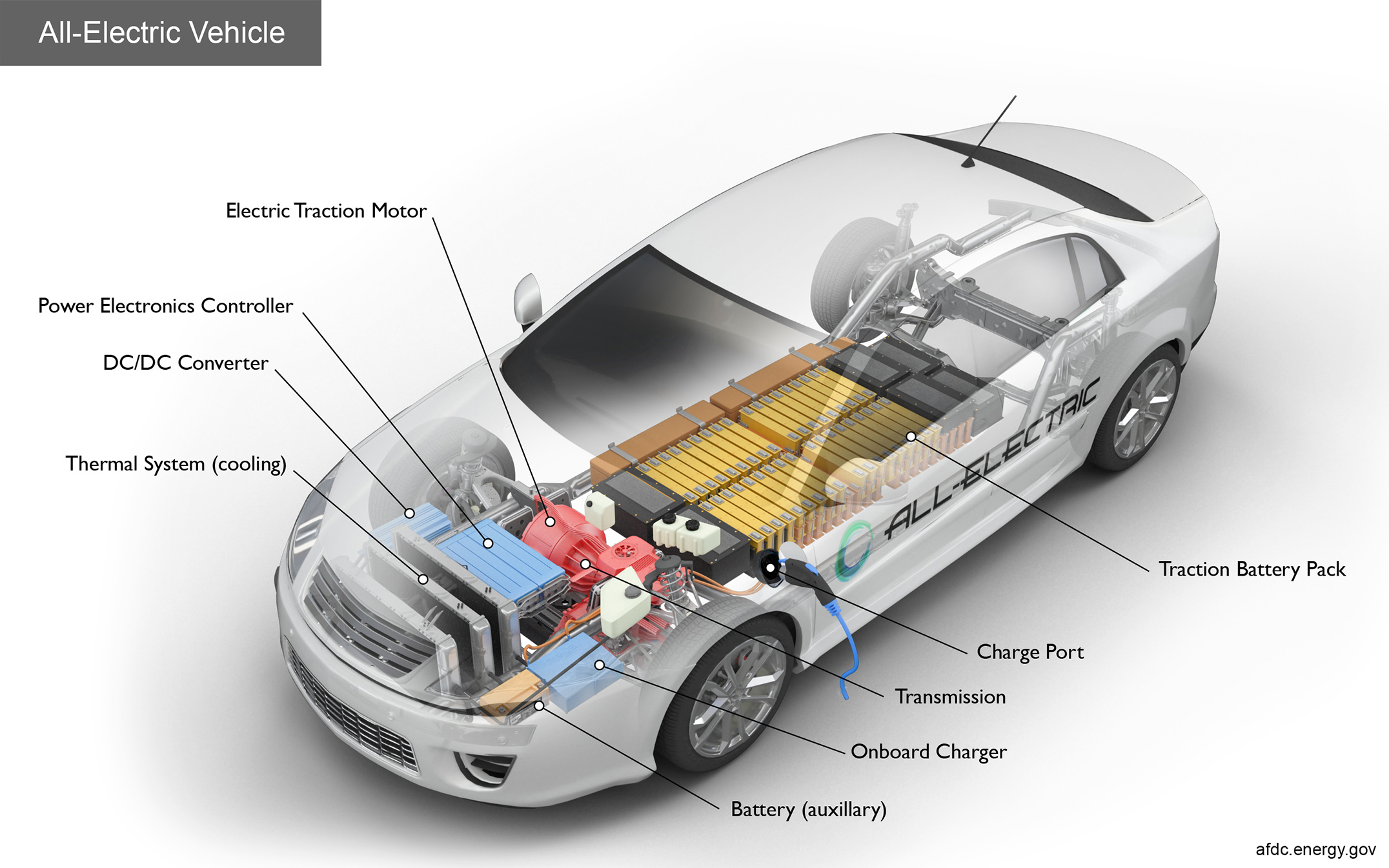
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Disadvantages Of An Electric Car?
Electric cars can have limited range and longer charging times. Battery replacement costs are high. Charging infrastructure might be insufficient in some areas. Weather conditions can affect battery performance. Initial purchase price is often higher compared to traditional vehicles.
Is It Still Free To Charge An Electric Car?
Charging an electric car isn’t always free. Some public stations offer complimentary charging, while others charge fees. Costs vary by location and provider. Always check local stations for fees or free options. Installing a home charger incurs upfront costs but can save money in the long run.
Do Electric Cars Need Oil Changes?
Electric cars do not need oil changes. They use electric motors, which require no engine oil. Instead, electric vehicles need periodic maintenance on components like brakes, tires, and batteries. Regular software updates and coolant checks are essential for optimal performance.
Electric cars offer a cleaner, low-maintenance alternative to traditional vehicles.
How Long Do Electric Car Batteries Last?
Electric car batteries typically last 10-20 years. Battery lifespan varies based on usage and environmental factors. Regular maintenance and proper charging extend battery life. Most manufacturers offer warranties covering 8 years or 100,000 miles. Advances in technology continue to improve battery durability and longevity.
Conclusion
Electric cars are changing how we think about driving. They offer cleaner transport with fewer emissions. Their motors run quietly, adding peace to daily commutes. Charging stations are popping up everywhere, making refueling easier. While battery technology continues to improve, electric cars become more practical.
They promise a future with less noise and cleaner air. Understanding how they work can help make informed choices. Electric cars aren’t just a trend; they’re a step towards a sustainable future. Exploring them now prepares us for the changes ahead.
Drive into a greener tomorrow.
Table of Contents







Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.