A dirt bike converts fuel into wheel power using engine combustion, gears, and traction.
Curious minds always ask, how does a dirt bike work? I have tuned, ridden, and raced them for years, from tight woods to sandy tracks. In this guide, I will break it down in simple terms. We will go from throttle twist to dirt rooster tails so you can see each part do its job. If you want a clear answer to how does a dirt bike work, you are in the right place.

The big picture: from throttle to rear wheel
How does a dirt bike work? It starts when you open the throttle. The throttle lets in more air and fuel. The engine burns that mix. The burn pushes a piston down. The crankshaft spins. Gears multiply the force. The chain turns the rear wheel. The tire grabs dirt and moves you forward.
Here is the flow in plain steps:
- Air and fuel enter the engine.
- The spark plug lights the mix.
- The piston drives the crankshaft.
- The clutch connects the engine to the gearbox.
- The gearbox sets the output speed.
- The chain and sprockets drive the rear wheel.
- The tire makes traction with the ground.
When riders ask, how does a dirt bike work, I show them this chain of events. It is like a relay race from airbox to tire patch.
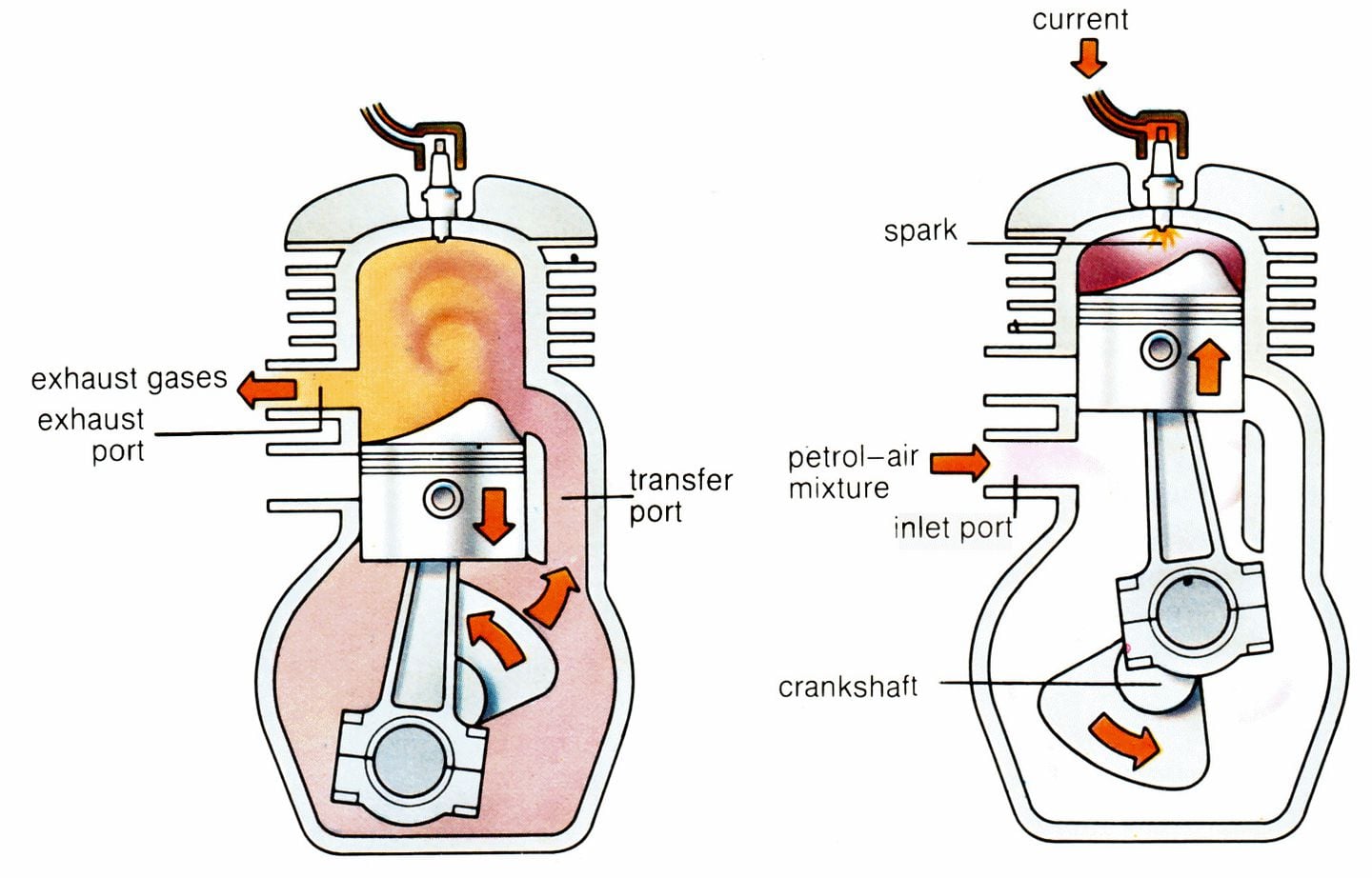
Engine basics: 2-stroke vs 4-stroke
Two main engine types power dirt bikes. Each feels different on the trail.
2-stroke engines:
- One power stroke every crank turn.
- Simple design with ports and a reed valve.
- Light weight and quick hit of power.
- Needs premix or oil injection.
4-stroke engines:
- One power stroke every two crank turns.
- Uses valves, cams, and a timing chain.
- Broader power and easy traction.
- Runs engine oil in the crankcase.
How does a dirt bike work when you compare both? A 2-stroke makes a sharp powerband. A 4-stroke spreads power smooth. On slick clay, I pick a 4-stroke for grip. In tight woods, a light 2-stroke saves energy.
Fuel, air, and spark: making power you can use
Every burn needs the right mix. The carburetor or fuel injection sets this mix. The air filter keeps dust out. The spark plug lights the charge at the right time.
- Carburetor bikes use jets and needles to meter fuel.
- Fuel-injected bikes use sensors and an ECU to control fuel and timing.
- The ignition system uses a CDI or ECU to fire the spark.
If you ever ask, how does a dirt bike work when climbing a hill, think airflow. More air needs more fuel. That is why bikes feel lean at high altitude. I swap jets or map settings on trips to the mountains.

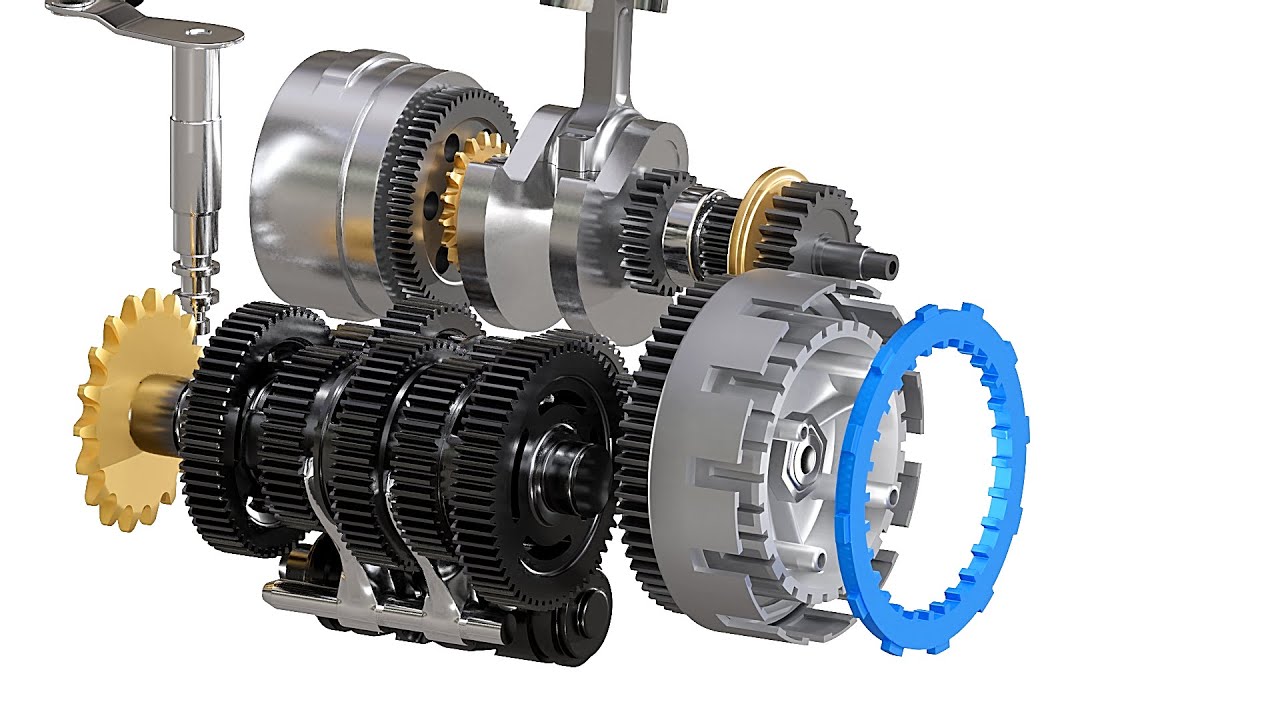
Clutch, gearbox, and shifting
The clutch lets you control engine power. Pull the lever, and plates slip. Let it out, and the plates grab. You can feed in power smooth on slippery roots.
The gearbox turns engine speed into usable wheel speed. Lower gears give more torque at the wheel. Higher gears give more speed. How does a dirt bike work in a tight turn? I use the clutch to keep the revs up, then shift early to hook up.
- Use two fingers on the clutch for better feel.
- Shift before the rev limiter for smooth drive.
- Change sprocket sizes to fine tune gear feel.

Chain, sprockets, and traction
Power leaves the gearbox at the front sprocket. The chain carries it to the rear sprocket. Sprocket sizes change how the bike launches and cruises.
- Larger rear sprocket gives quicker drive.
- Smaller rear sprocket gives more top speed.
- Keep the chain clean, lubed, and at the right slack.
How does a dirt bike work when the dirt is deep and soft? Short gearing and fresh knobbies help the tire bite. I also slide back on the seat to load the rear tire for extra grip.

Suspension and chassis geometry
Suspension keeps the tires on the ground. Forks control the front. A shock controls the rear. Springs hold the bike up. Oil damping slows the motion.
- Sag sets ride height. Set rider sag before any changes.
- Compression damping resists bottoming.
- Rebound damping controls kick-back.
How does a dirt bike work when you hit whoops? The fork and shock cycle fast to track the ground. If rebound is too slow, the bike packs down. If too fast, it bucks. I tune clickers a few clicks at a time and log each change.

Brakes, wheels, and tires
Brakes turn speed into heat. Front brake does most of the work. Rear brake helps steer and settle the bike. Big rotors and good pads raise control.
Tires are your only contact with the earth. Choose the right pattern and compound for the soil. How does a dirt bike work in sand? Use a paddle or a deep scoop tread. Drop pressure a little for a bigger footprint.
- Use two fingers on the front brake for feel.
- Bed in new pads and rotors.
- Check spoke tension often.
Cooling and lubrication
Engines make heat and need oil. Many dirt bikes are liquid cooled. Radiators and coolant move heat away. Oil lowers friction and carries debris to the filter.
- Keep radiators clean and straight.
- Use the oil grade in the owner manual.
- Change oil on time, often 5 to 15 hours based on riding.
How does a dirt bike work under slow, tight riding? Airflow is low, so heat rises. I add a fan kit on enduro bikes and avoid long idles.

Electronics and starting systems
Modern bikes use an ECU to control fuel and spark. Traction maps and launch control are common on race models. Electric start uses a battery and a starter motor. Kick start is lighter but needs skill.
How does a dirt bike work when maps change? A softer map tames the hit in slick mud. A hard map adds snap on deep loam. I keep a handlebar map switch for quick changes mid lap.
Riding dynamics and control
Your body is part of the system. Weight shifts change traction. Smooth throttle keeps the tire hooked. Vision guides line choice.
- Stand up over bumps to let legs act as springs.
- Look ahead and plan exits early.
- Breathe and relax your grip.
How does a dirt bike work best in real life? It listens to calm inputs. On my first enduro, I fought the bike. When I relaxed, the bike found flow.
Maintenance that keeps it working
A well-kept bike works better and lasts longer. Service schedules in manuals are there for a reason. Small jobs prevent big bills.
- Clean and oil the air filter every ride in dust.
- Check chain slack and lube after each wash.
- Torque critical bolts like axle nuts and triple clamp bolts.
- Bleed brakes and flush fluid on a set schedule.
- Check valve clearances on 4-strokes at the interval.
How does a dirt bike work after months of hard use? It works great if you keep to the basics. I track hours on the bars and log each service.
Common mistakes, tips, and setup
Avoid these common pitfalls I see in the pits.
- Running old fuel. Use fresh fuel and drain bowls if stored.
- Over-tight chains. Set correct slack to save bearings and seals.
- Ignoring sag. Set it with full gear on.
- Wrong tire for the terrain. Match tire to soil type.
- Skipping warm-up. Bring temp up before full throttle.
How does a dirt bike work when set up right? It feels calm and planted. It turns with little effort. It stops with less drama. Small changes add up fast.
Troubleshooting in the field
Bikes talk when something is off. Learn the signs.
- Hard starting when hot may mean valves are tight on a 4-stroke.
- Bog on quick throttle may mean lean jetting or a dirty injector.
- Sputter at high rpm may be a weak spark plug or coil.
- Overheating may be low coolant or clogged fins.
- Chain snatch may be worn sprockets or kinks.
How does a dirt bike work when you fix the root cause? It starts first press or first kick. It pulls clean. It runs cool. I carry spare plugs, a link, and a small jet kit on long rides.
Frequently Asked Questions of How does a dirt bike work?
How does a dirt bike work in simple terms?
It burns fuel to push a piston, spins a crank, and drives the wheel through gears and a chain. The tire grabs dirt to move you forward.
How does a dirt bike work differently from a street bike?
It uses long-travel suspension, knobby tires, and off-road gearing. The focus is on traction and control on rough ground.
How does a dirt bike work when it is a 2-stroke?
It fires every crank turn and uses ports, a reed valve, and premix oiling. Power comes on fast with a strong powerband.
How does a dirt bike work with fuel injection?
Sensors tell the ECU how much fuel and spark to use. It adjusts for temperature and altitude, giving smooth starts and steady power.
How does a dirt bike work to create traction?
Suspension keeps the tire on the ground, and throttle control avoids spin. Tire choice and pressure finish the job.
How does a dirt bike work when the clutch is slipping?
The clutch plates do not fully grab, so power is lost. Adjust the cable, check free play, and replace worn plates if needed.
How does a dirt bike work on steep hills?
Use the right gear, steady throttle, and body weight forward. Keep momentum and avoid sudden chops that break traction.
Conclusion
You now have a clear, ground-up view of how does a dirt bike work. From air and fuel to sparks and gears, every part plays a simple role. Put those roles together, and the machine becomes a tool you can trust.
Take one idea from this guide and apply it on your next ride. Set sag, pick a map, or clean the filter. Small wins stack up fast. Want more deep dives? Subscribe, ask a question, or share your setup in the comments.
Table of Contents






Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.